export declare type 和 export type 的区别
export declare type 和 export type 的主要区别在于它们在 TypeScript 代码中的作用。export type 用于定义和导出类型,而 export declare type 用于声明一个在其他地方定义的类型。
假设你正在做一个大型项目,需要很多人一起写代码。为了避免大家写的代码互相冲突,需要提前约定好一些规范。type 就类似于这种规范,它定义了数据应该长什么样。
export type: 就像你自己制定了一条规范,并且告诉其他人:“嘿,我这里有个新规范,你们也可以用!” 例如,你定义了一个UserType,规定了用户信息应该包含姓名和年龄。然后你把它export出去,其他开发者就可以在他们的代码里使用你的UserType了。export declare type: 就像你听说别人已经制定了一条规范,你想在你的代码里用,但是你手里没有这条规范的具体内容。所以你就declare一下,告诉编译器:“我知道有这么个规范,我会在别的地方找到它的,你先别报错。” 例如,某个外部库定义了一个FancyDataType,你不知道它的具体结构,但你想用它。你就可以export declare type FancyDataType,这样编译器就不会因为找不到FancyDataType的定义而报错了。 等到代码真正运行的时候,这个外部库会提供FancyDataType的具体实现。
解释下面
类型定义

①
<T extends MaybeRef<Record<string, any> | string> = string>: 这是一个泛型类型参数T。它被约束为扩展MaybeRef<Record<string, any> | string>。这意味着T可以是以下几种类型:- 一个
string:表示一个简单的字段名。 Record<string, any>:一个对象,其中键是字符串(字段名),值可以是任何类型。- MaybeRef 是一个用于处理 Vue 响应式类型的概念。等同于
type MaybeRef<T> = T | Ref<T>; = string部分将T的默认类型设置为string
- 一个
②
Partial<...>: 这使得记录的所有属性都是可选的。因此,不必为每个字段都定义规则Record用于创建key-value类型- 这里key =
UnwrapRef<T> extends string ? UnwrapRef<T> : FieldPath<UnwrapRef<T>> - 这里value =
Arrayable<FormItemRule>>
- 这里key =
UnwrapRef<T>是一个条件类型,通常用于 Vue 3 中。UnwrapRef<T>的作用是从响应式引用中提取出原始值。Arrayable:export declare type Arrayable<T> = T | T[];
Partial
Partial 是一个非常有用的工具类型,允许我们在处理对象时更加灵活,特别是在更新或传递部分属性时。通过使用 Partial<T>,我们可以避免定义多个接口来处理完整对象和部分对象之间的区别。
用法
通过 Partial<T> 类型,可以将一个类型的所有属性转换为可选属性。例如:
interface User {
id: number;
name: string;
email: string;
}
// 使用 Partial 将 User 的属性全部变为可选属性
const updateUser = (userId: number, userUpdates: Partial<User>) => {
// 逻辑处理
};
// 调用 updateUser 时,可以只传递部分属性
updateUser(1, { name: 'Alice' });
updateUser(2, { email: 'bob@example.com' });
updateUser(3, { name: 'Charlie', email: 'charlie@example.com' });interface User {
id: number;
name: string;
email: string;
}
// 使用 Partial 将 User 的属性全部变为可选属性
const updateUser = (userId: number, userUpdates: Partial<User>) => {
// 逻辑处理
};
// 调用 updateUser 时,可以只传递部分属性
updateUser(1, { name: 'Alice' });
updateUser(2, { email: 'bob@example.com' });
updateUser(3, { name: 'Charlie', email: 'charlie@example.com' });在上面的例子中,userUpdates 参数的类型是 Partial<User>,因此你可以只传递你希望更新的属性,而不需要提供 User 类型的所有属性。
实现原理
Partial 类型的实现原理如下:
type Partial<T> = {
[P in keyof T]?: T[P];
};type Partial<T> = {
[P in keyof T]?: T[P];
};这里,keyof T 用于获取类型 T 的所有属性的键(keys),然后通过映射类型(mapped types)将每个属性后面加上问号 ?,表示这些属性是可选的。
namespace
在 TypeScript 中,namespace 是一种用于组织代码的机制。通过使用命名空间,可以将相关的代码分组,避免命名冲突,并增强代码的可维护性。使用示例:
namespace MathUtils {
export function add(a: number, b: number): number {
return a + b;
}
}
// 调用
MathUtils.add()namespace MathUtils {
export function add(a: number, b: number): number {
return a + b;
}
}
// 调用
MathUtils.add()Pick
Pick<T, K> 是 TypeScript 中一个非常有用的内置工具类型,它的主要作用是从一个已有的类型 T 中挑选出指定的属性集合 K,并构建一个新的类型。
type Person = {
name: string;
age: number;
};
// 使用 Pick 从 Person 类型中挑选出 name 和 age 属性
type PersonNameAndAge = Pick<Person, "name" | "age">;
const zzz: PersonNameAndAge = {
name: "123",
age: 12,
};
if (import.meta.main) {
console.log(zzz);
}type Person = {
name: string;
age: number;
};
// 使用 Pick 从 Person 类型中挑选出 name 和 age 属性
type PersonNameAndAge = Pick<Person, "name" | "age">;
const zzz: PersonNameAndAge = {
name: "123",
age: 12,
};
if (import.meta.main) {
console.log(zzz);
}代码实现:
type MyPick<T, K extends keyof T> = {
[V in K]: T[V];
};type MyPick<T, K extends keyof T> = {
[V in K]: T[V];
};这里 keyof PersonNameAndAge 等同于 'name' | 'age'。
Readonly
它的作用是接收一个泛型参数 T ,并返回一个完全一样的类型,只是所有属性都会被 readonly 所修饰。也就是不可以对该对象的属性重新赋值。
interface Todo {
title: string;
description: string;
}
const todo: Readonly<Todo> = {
title: "Eat",
description: "Eat some food",
};interface Todo {
title: string;
description: string;
}
const todo: Readonly<Todo> = {
title: "Eat",
description: "Eat some food",
};readonly:

类型实现:
type MyReadonly<T> = {
readonly [K in keyof T]: T[K];
};type MyReadonly<T> = {
readonly [K in keyof T]: T[K];
};as const

可以看到增加了 readonly
number 在映射类型中使用
number可以用来定义数字索引的属性类型。
例如元组类型转对象类型

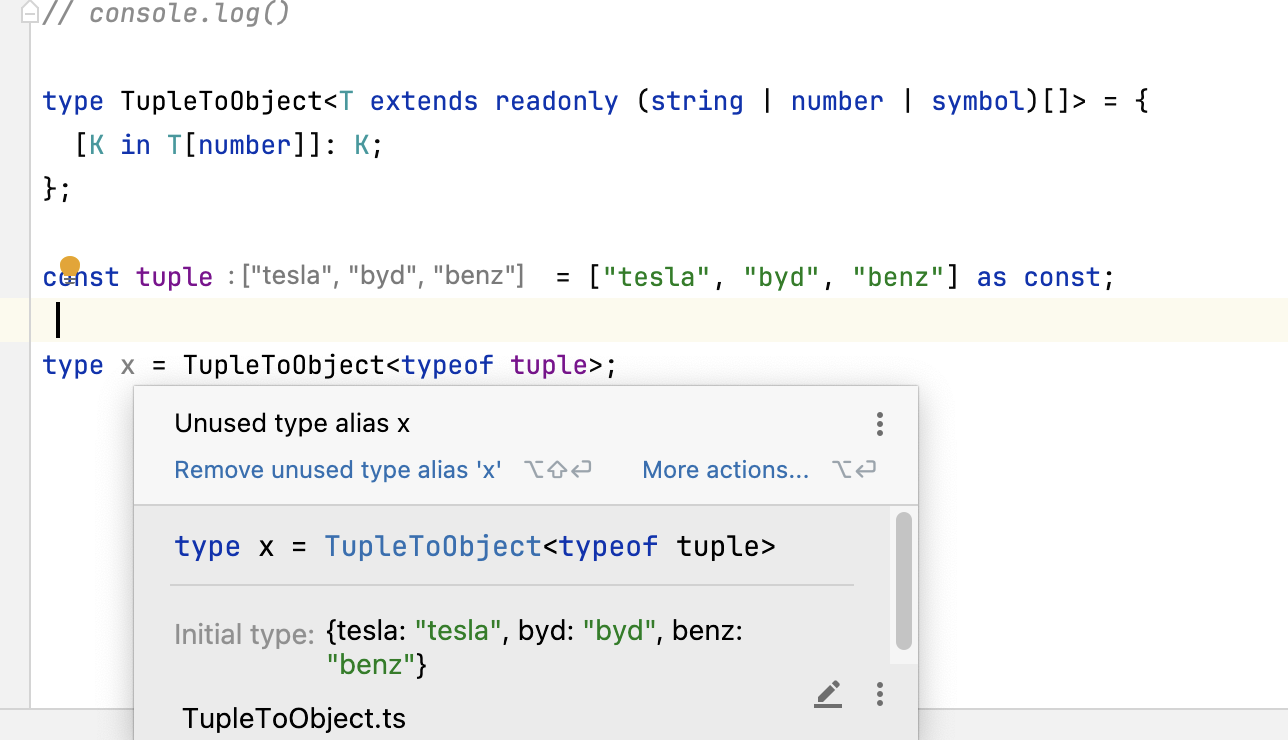
答案:
type TupleToObject<T extends readonly (string | number | symbol)[]> = {
[K in T[number]]: K;
};type TupleToObject<T extends readonly (string | number | symbol)[]> = {
[K in T[number]]: K;
};
判断数组为空
几种写法:
extends []T["length"] extends 0T[number] extends never
type First<T extends (string | number)[]> = T extends [] ? never : T[0];
type First2<T extends (string | number)[]> = T["length"] extends 0 ? never
: T[0];
type First3<T extends (string | number)[]> = T[number] extends never ? never : T[0];type First<T extends (string | number)[]> = T extends [] ? never : T[0];
type First2<T extends (string | number)[]> = T["length"] extends 0 ? never
: T[0];
type First3<T extends (string | number)[]> = T[number] extends never ? never : T[0];Exclude
手动实现:

总结 Conditional Types
Conditional Types提供了一种在TypeScript类型系统中执行简单逻辑的方法。这绝对是一个高级功能,而且,在日常代码中不需要使用它是非常可行的。
// Where the condition is whether a type extends an
// expression, and if so what type should be returned.
A extends B ? C : D// Where the condition is whether a type extends an
// expression, and if so what type should be returned.
A extends B ? C : D为了简洁起见,我们将使用单个字母表示泛型
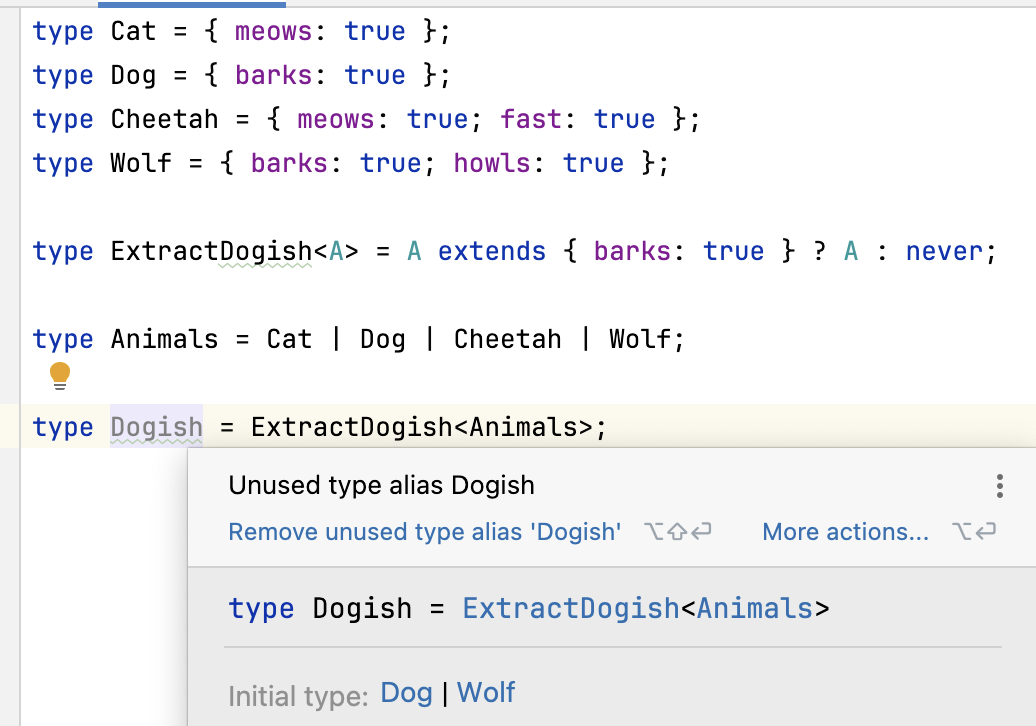
type Cat = { meows: true };
type Dog = { barks: true };
type Cheetah = { meows: true; fast: true };
type Wolf = { barks: true; howls: true };type Cat = { meows: true };
type Dog = { barks: true };
type Cheetah = { meows: true; fast: true };
type Wolf = { barks: true; howls: true };创建条件类型,提取满足barks的动物:
type ExtractDogish<A> = A extends { barks: true } ? A : never;
type NeverCat = ExtractDogish<Cat>;
type Wolfish = ExtractDogish<Wolf>;type ExtractDogish<A> = A extends { barks: true } ? A : never;
type NeverCat = ExtractDogish<Cat>;
type Wolfish = ExtractDogish<Wolf>;如果想使用多种类型组合:
type Animals = Cat | Dog | Cheetah | Wolf;type Animals = Cat | Dog | Cheetah | Wolf;可以将ExtractDogish用于联合类型:
type Dogish = ExtractDogish<Animals>;
// = ExtractDogish<Cat> | ExtractDogish<Dog> |
// ExtractDogish<Cheetah> | ExtractDogish<Wolf>
// = never | Dog | never | Wolf
// = Dog | Wolftype Dogish = ExtractDogish<Animals>;
// = ExtractDogish<Cat> | ExtractDogish<Dog> |
// ExtractDogish<Cheetah> | ExtractDogish<Wolf>
// = never | Dog | never | Wolf
// = Dog | Wolf